Did you know that injection molding is transforming the medical device industry? This advanced process empowers designers to create high-quality and cost-effective products, ranging from common medical items to highly regulated devices. As products move through various stages of development—from initial prototyping to full-scale production-they must consistently meet stringent compliance, safety, and functionality standards. This ensures that each medical device aligns with critical industry requirements at every step.
If you’re considering taking the next step in medical injection molding, this article will guide you through 4 key considerations in medical injection molding, from understanding device classifications and regulations to selecting suitable materials and preparing your design.
Key Considerations in Medical Injection Molding
1. Regulatory Compliance: Meeting Corresponding Standards
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines in the U.S. mandate rigorous tracking and documentation at every production stage to guarantee the traceability of each component. Meanwhile, Medical Device Regulation (MDR) standards in the EU emphasize consistent product safety across the device’s entire lifecycle, pushing manufacturers to follow stringent standards.
Medical devices are divided into three classifications, by both FDA and MDR, based on associated risk, each with specific regulatory requirements:
Class I Medical Devices: These low-risk devices pose minimal harm to users, often including items like bandages, gloves, and hand-held surgical instruments. Regulatory requirements are relatively basic, focusing mainly on general safety and quality.
Class II Medical Devices: Moderate-risk devices, such as syringes, infusion pumps, and diagnostic equipment, require additional regulatory controls. These may involve special labeling, performance standards, and post-market supervision.
Class III Medical Devices: High-risk devices, including pacemakers, defibrillators, and implants, require the highest level of regulatory supervision. This includes rigorous premarket approval, extensive testing, and clinical trials to confirm safety and effectiveness.
For instance, a diagnostic device used for detecting infectious diseases needs each plastic component to withstand various sterilization processes without degrading or releasing harmful substances. Even minor contamination could compromise the device’s accuracy or pose risks to patients, underscoring the importance of these strict regulatory standards. Ensuring regulatory compliance is essential in medical injection molding, as incorrect categorization or non-compliance can lead to delays, increased costs, and a longer time to market.
2. Certifications: Guaranteeing Quality and Safety
Certification is a standard, ensuring the products meet or exceed industry requirements. Key certifications in the medical industry include:

13485
ISO 13485: This certification ensures a quality management system is in place, maintaining consistency across production batches. For example, if producing IV systems or ventilators, ISO 13485 certification is critical.

10933
ISO 10933: For parts that come in direct contact with bodily fluids or tissues, ISO 10993 ensures biocompatibility. This certification is essential when manufacturing parts such as catheter tips or implantable device housings, where material safety directly impacts patient health.

14644
ISO 14644: This cleanroom certification is crucial for preventing contamination. A cleanroom-certified facility, for instance, can safely produce surgical device components that require a sterile environment, ensuring they meet hospital and surgical standards.

14971
ISO 14971: ISO 14971: This certification ensures risk management processes are in place, crucial for medical devices. For example, it’s essential when manufacturing parts like infusion pumps or pacemakers, where rigorous risk controls are necessary to protect patient safety.
3. Material Selection: Biocompatibility and Durability
Choosing materials for medical applications involves considerations beyond standard injection molding. Examples include:
• Polycarbonate (PC): Due to its strength and transparency, often used for housing devices requiring internal visibility, such as blood analyzers.
• Polyethylene (PE): Known for chemical resistance and flexibility, PE is used in IV bags and tubing, ensuring durability and low moisture absorption.
• Polypropylene (PP): With strong impact resistance and sterilization stability, PP is used in syringes and medical containers, offering long-term reliability.
• Polystyrene (PS): Widely used for disposable labware, PS offers rigidity, transparency, and easy sterilization, making it suitable for laboratory applications.
• Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK): Widely used in implantable devices due to its strength, stability under sterilization, and biocompatibility.
• Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): Its flexibility makes it suitable for soft-touch surgical instrument handles that withstand repeated sterilization.
Every material choice has specific trade-offs. For instance, while PE and PP are cost-effective and chemically resistant, they might lack the strength needed for parts exposed to high-stress environments. Therefore, understanding these nuances helps in material selection, optimizing for both performance and cost. Click Here to explore more material choices.
4. Prototyping to Production: Ensuring a Smooth Transition
Transitioning from prototypes to full-scale production isn’t always straightforward. During prototyping, designs may feature thinner walls or more complex geometries than standard injection molding processes can easily reproduce at scale. For example, a prototype with sharp corners that’s achievable created by vacuum casting process, but requires design optimization, such as adding radii, and adding draft angle for efficient injection molding without sacrificing quality. When scaling up, an experienced injection molding partner with expertise and capabilities can help optimize these designs for manufacturability without compromising on quality. At RPWORLD, we assist clients in this crucial transition, helping optimize part design, select the most suitable materials, finishing options and more to support efficient and regulatory-compliant production.
Why Choose RPWORLD Injection Molding for Your Medical Development
At RPWORLD, we integrate material expertise, one-stop manufacturing services, in-depth DFM analysis and ISO-certified process to help bring medical devices to market faster. Our services cover the entire lifecycle-from prototyping to mass production-tailoring to meet the unique needs of each medical device.
• 20+ years of experience in medical device injection molding, from prototyping to end-use production.
• Mold flow analysis, and in-house tools design and fabrication.
• A wide variety of post-processing options to perfect your parts.
RPWORLD Injection Molding Service
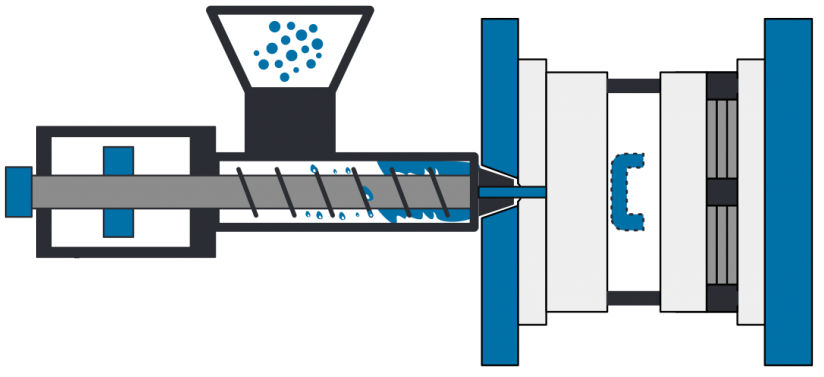
• Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidance, including design optimization, material selection, finishing selection and more to avoid costly rework and save time up to 80%.
• State-of-the-art
quality inspection equipment and stringent
quality control including real-time process monitoring to ensure consistency.
Ready to elevate your medical device manufacturing? Connect with
RPWORLD today and see how we can support your production journey from concept to reality.







